Researching ZARA’s customer data to identify challenges that contribute to drop-off rates.
10 mins read • User Research
Research Method 1: Need Finding
When coronavirus affected the offline shopping experience worldwide, it hurt ZARA the most. With approximately 1200 offline outlets being shut down, ZARA customers couldn’t resist the shopping urge, went online to shop, and weren’t convinced enough to complete purchases.
Users vented out about bad UX, on Reddit comments and wrote articles on Medium.
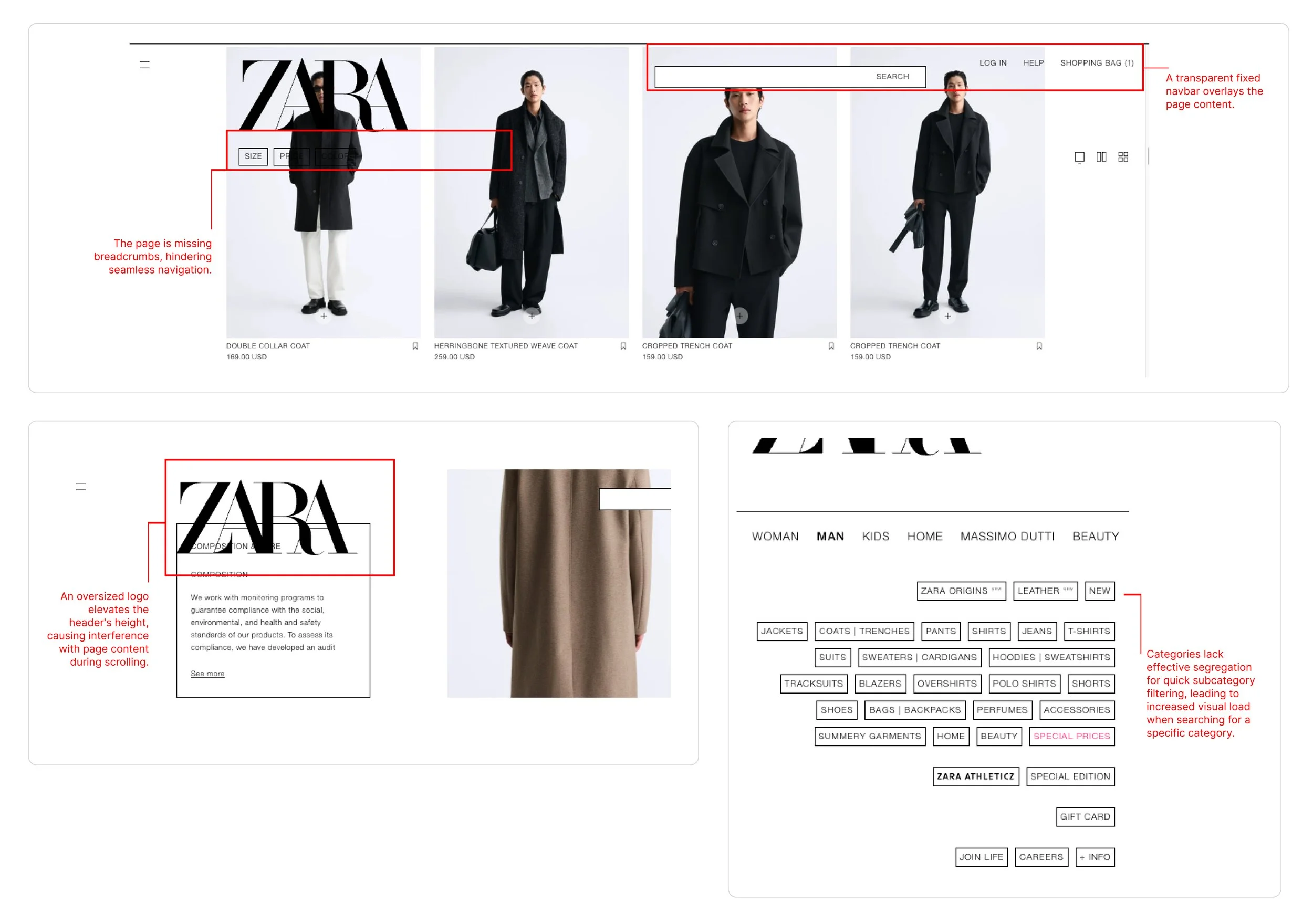
Low-contrast navigation patterns sitting on busy images isn’t the ideal FTUX when users are exploring products.
If you want your customer to explore your offerings, they shouldn’t be searching for certain areas like the search bar, navigation links, and product categories.
Research Method 2: Performing Heuristics Evaluation
Team
Karthik Sharma
Diksha Rawat
Shikha Singh
Harshveen Kalsi
Tasks
1. Browsing products by category.
2. Searching for a specific item.
3. Adding items to the cart.
4. Completing the checkout process.
Risk Criteria
1. Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
2. Frequency (# occurrence)
Results
Research Method 1: Performing Heuristics Evaluation
Team
Karthik Sharma
Diksha Rawat
Shikha Singh
Harshveen Kalsi
Tasks
1. Browsing products by category.
2. Searching for a specific item.
3. Adding items to the cart.
4. Completing the checkout process.
Risk Criteria
1. Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
2. Frequency (# occurrence)
Results
Conduct a heuristic evaluation of Zara’s website to identify accessibility barriers
Connect with users and understand experience painpoints
Challenges
“In 2021, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern…”
When coronavirus affected the offline shopping experience worldwide, people couldn’t resist the urge to shop online, and that’s when the reality hit hard. With approximately 1200 offline outlets being shut down, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern.
Refer to the January 2023 web portal screenshots
Busy Images combined with low-contrast navigation patterns increase the exploration journey for first-time users. Especially when you want the customer to explore your product offerings, they shouldn’t be searching for certain areas — the search bar, navigation links, and categories.
Complex Navigation
The website’s layout can be unintuitive, making it difficult for users to find specific categories or products efficiently.
According to Sciencedirect.com, “…navigational links should be visible within 5 seconds…”
Over-Reliance on Images
Zara heavily emphasizes visual elements, sometimes at the expense of clear text descriptions, making it harder for users to scan and browse quickly.
Research
Research Hypothesis
Implementing usability and accessibility improvements based on WCAG 2.1 standards will result in higher user satisfaction and task completion rates for Zara’s e-commerce website.
Research Methods
(A) Heuristic Evaluation
Team
Karthik Sharma
Diksha Rawat
Shikha Singh
Harshveen Kalsi
Tasks
1. Browsing products by category.
2. Searching for a specific item.
3. Adding items to the cart.
4. Completing the checkout process.
The website was rigorously tested against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards, focusing on key principles of perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness.
(B) User Interviews
Objective
To understand user behaviors and pain points when using Zara’s website.
Participants
5 participants (2 female, 3 male) aged 22–25, representing Zara’s target demographic.
Sample Questions
How often do you order from ZARA?
Can you describe your experience with ordering?
Did you spend more time than expected ordering online?
Are there any significant roadblocks in your way?
What are your views on the mobile app?
Sample Tasks
Add a product from the “x” category to your cart and finalize the payment.
Navigate to the “y” part of the platform
Raise a platform concern
Can you browse the “z” category products
Ethical Considerations
Informed Consent
All participants provided informed consent before participating in interviews and surveys.Anonymity
Participant data was anonymized to protect privacy.Data Security: Survey and interview data were stored securely and used only for research purposes.
Sample Empathy Mapping
Here’s a sample empathy map that I created to capture what the user said, felt, did, and thought during the interviews. This map helped us pinpoint the sources of user frustration.
(C) Feedback Analysis
We dived deep into customer reviews to identify user emotion patterns towards the online presence to find that Zara had a 2.08 star rating from 1,132 reviews, indicating that most customers are generally dissatisfied with their online platform experience.
”…Zara ranked 43th among Best Global Brands in the year 2023. It was ranked 25th in 2018 and has kept dropping ever since…”
Code Inspection
On inspecting the web portal code to identify the design intricacies, we found that certain spacings, layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly,y the choice of background image used was interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Research Findings
The evaluation revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation and checkout processes.
Users struggled with ambiguous labels, inconsistent design, and a lack of feedback, leading to frustration and task abandonment.
These findings align with previous research on e-commerce usability, emphasizing the importance of clear navigation and error prevention., Layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly, the choice of background image used, were interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Solution
Improved Navigation
Updated layout features ample white space and evenly distributed information essential for guiding users through their intended actions.
Onboarding starts with Information Clarity.
As part of our UX revamp, the website now features an improved onboarding process. After each development release, new features that benefit the user will be presented to returning customers through modals. We chose modals because they direct the user’s attention to key information, allowing them to focus on the content while keeping the background out of focus..
Feature Improvement: Sticky Pane for Major User Actions
To enhance usability and streamline the user experience, we propose the implementation of a sticky pane on the right side of the website. This pane will occupy 20% of the screen real estate and provide quick access to the most commonly performed tasks, ensuring that key functionalities are always within reach. The sticky pane will remain visible as users scroll, offering consistent and intuitive navigation.
Improved Accessibility
Key actions are always visible, reducing the cognitive load on users.
Enhanced Efficiency
Users can perform common tasks without navigating through multiple pages.
Consistent Navigation
The sticky pane ensures that essential functionalities are always accessible, regardless of where the user is on the website.
User-Centric Design
By prioritizing the most frequently used tasks, the design aligns with user needs and behaviors.
The same usability task results showed a user confidence boost of 60% on average.
We carried out moderated usability testing, focusing on task-based evaluation and comparison to the original version, to validate the prototype's usability and functionality.
Participants were tasked with comparing the navigation and overall layout of Zara's website to our prototype. Subsequently, they were assigned specific tasks, such as locating an item and placing an order, allowing us to assess the user experience comprehensively.
Learnings
Enhancing an interface doesn't always necessitate an extensive budget or a complete overhaul. Sometimes, minor adjustments can wield a substantial impact.
This paper served as a reminder that even prominent brands with successful products and services can undergo significant improvement without incurring exorbitant costs.
Conclusion
This study employed a mixed-methods approach to evaluate the usability of Zara’s website, combining heuristic evaluation, user interviews, and surveys. The findings revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation, checkout, and product discovery. By addressing these issues, Zara can enhance the user experience, increase customer satisfaction, and improve conversion rates. Future research could include usability testing with prototypes to validate the proposed recommendations.
References
Nielsen, J. (1994). Usability Engineering. Morgan Kaufmann.
Norman, D. A. (2013). The Design of Everyday Things. Basic Books.
Rubin, J., & Chisnell, D. (2008). Handbook of Usability Testing. Wiley.
Additional sources on UX research methodologies and e-commerce usability.
Propose design solutions to address these barriers and painpoints.
Risk Criteria
1. Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
2. Frequency (# occurrence)
Onboarding Prototype
Post user interviews and usability testing, we had a good understanding of the problem statement and the solutions required for the same. So we started working on the prototype. The tool used for designing the prototype was Moqups.
Background
For a research project at Northeastern University, we focused on the critical role of accessibility in driving the online dropoff and retention rates.
We selected ZARA for this project because of its global presence and also, for its recent 44% sales drop during COVID.
Team
Kartik Sharma, Diksha Rawat, Shikha Singh
Our Hypothesis
“Lack of accessibility standards & poor UX significantly contributed to high drop-off rates and incomplete purchases at ZARA.”
What did we know?
When coronavirus affected the offline shopping experience worldwide, it hurt ZARA the most. With approximately 1200 offline outlets being shut down, ZARA customers couldn’t resist the shopping urge, went online to shop, and weren’t convinced enough to complete purchases.
Users vented out on Reddit comments and wrote articles on Medium.
It is important to pass WCAG 2.2 guidelines to ensure websites and digital content are accessible to individuals with disabilities, and stay ahead of the evolving digital accessibility regulations, and avoid potential legal issues.
The identified accessibility issues were addressed through a comprehensive redesign, leading to improved usability and full compliance with WCAG 2.1 standards.
Selected Brand: Zara
Zara’s e-commerce website was selected as the use case due to its global reach and the critical importance of accessibility in its user experience. The website was evaluated against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards, with a focus on the core principles of perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness. The objectives include:
Conduct a heuristic evaluation of Zara’s website to identify accessibility barriers
Connect with users and understand experience painpoints
Challenges
“In 2021, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern…”
When coronavirus affected the offline shopping experience worldwide, people couldn’t resist the urge to shop online, and that’s when the reality hit hard. With approximately 1200 offline outlets being shut down, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern.
Refer to the January 2023 web portal screenshots
Busy Images combined with low-contrast navigation patterns increase the exploration journey for first-time users. Especially when you want the customer to explore your product offerings, they shouldn’t be searching for certain areas — the search bar, navigation links, and categories.
Complex Navigation
The website’s layout can be unintuitive, making it difficult for users to find specific categories or products efficiently.
According to Sciencedirect.com, “…navigational links should be visible within 5 seconds…”
Over-Reliance on Images
Zara heavily emphasizes visual elements, sometimes at the expense of clear text descriptions, making it harder for users to scan and browse quickly.
Research
Research Hypothesis
Implementing usability and accessibility improvements based on WCAG 2.1 standards will result in higher user satisfaction and task completion rates for Zara’s e-commerce website.
Research Methods
(A) Heuristic Evaluation
Team
Karthik Sharma
Diksha Rawat
Shikha Singh
Harshveen Kalsi
Tasks
1. Browsing products by category.
2. Searching for a specific item.
3. Adding items to the cart.
4. Completing the checkout process.
The website was rigorously tested against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards, focusing on key principles of perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness.
(B) User Interviews
Objective
To understand user behaviors and pain points when using Zara’s website.
Participants
5 participants (2 female, 3 male) aged 22–25, representing Zara’s target demographic.
Sample Questions
How often do you order from ZARA?
Can you describe your experience with ordering?
Did you spend more time than expected ordering online?
Are there any significant roadblocks in your way?
What are your views on the mobile app?
Sample Tasks
Add a product from the “x” category to your cart and finalize the payment.
Navigate to the “y” part of the platform
Raise a platform concern
Can you browse the “z” category products
Ethical Considerations
Informed Consent
All participants provided informed consent before participating in interviews and surveys.Anonymity
Participant data was anonymized to protect privacy.Data Security: Survey and interview data were stored securely and used only for research purposes.
Sample Empathy Mapping
Here’s a sample empathy map that I created to capture what the user said, felt, did, and thought during the interviews. This map helped us pinpoint the sources of user frustration.
(C) Feedback Analysis
We dived deep into customer reviews to identify user emotion patterns towards the online presence to find that Zara had a 2.08 star rating from 1,132 reviews, indicating that most customers are generally dissatisfied with their online platform experience.
”…Zara ranked 43th among Best Global Brands in the year 2023. It was ranked 25th in 2018 and has kept dropping ever since…”
Code Inspection
On inspecting the web portal code to identify the design intricacies, we found that certain spacings, layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly,y the choice of background image used was interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Research Findings
The evaluation revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation and checkout processes.
Users struggled with ambiguous labels, inconsistent design, and a lack of feedback, leading to frustration and task abandonment.
These findings align with previous research on e-commerce usability, emphasizing the importance of clear navigation and error prevention., Layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly, the choice of background image used, were interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Solution
Improved Navigation
Updated layout features ample white space and evenly distributed information essential for guiding users through their intended actions.
Onboarding starts with Information Clarity.
As part of our UX revamp, the website now features an improved onboarding process. After each development release, new features that benefit the user will be presented to returning customers through modals. We chose modals because they direct the user’s attention to key information, allowing them to focus on the content while keeping the background out of focus..
Feature Improvement: Sticky Pane for Major User Actions
To enhance usability and streamline the user experience, we propose the implementation of a sticky pane on the right side of the website. This pane will occupy 20% of the screen real estate and provide quick access to the most commonly performed tasks, ensuring that key functionalities are always within reach. The sticky pane will remain visible as users scroll, offering consistent and intuitive navigation.
Improved Accessibility
Key actions are always visible, reducing the cognitive load on users.
Enhanced Efficiency
Users can perform common tasks without navigating through multiple pages.
Consistent Navigation
The sticky pane ensures that essential functionalities are always accessible, regardless of where the user is on the website.
User-Centric Design
By prioritizing the most frequently used tasks, the design aligns with user needs and behaviors.
The same usability task results showed a user confidence boost of 60% on average.
We carried out moderated usability testing, focusing on task-based evaluation and comparison to the original version, to validate the prototype's usability and functionality.
Participants were tasked with comparing the navigation and overall layout of Zara's website to our prototype. Subsequently, they were assigned specific tasks, such as locating an item and placing an order, allowing us to assess the user experience comprehensively.
Learnings
Enhancing an interface doesn't always necessitate an extensive budget or a complete overhaul. Sometimes, minor adjustments can wield a substantial impact.
This paper served as a reminder that even prominent brands with successful products and services can undergo significant improvement without incurring exorbitant costs.
Conclusion
This study employed a mixed-methods approach to evaluate the usability of Zara’s website, combining heuristic evaluation, user interviews, and surveys. The findings revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation, checkout, and product discovery. By addressing these issues, Zara can enhance the user experience, increase customer satisfaction, and improve conversion rates. Future research could include usability testing with prototypes to validate the proposed recommendations.
References
Nielsen, J. (1994). Usability Engineering. Morgan Kaufmann.
Norman, D. A. (2013). The Design of Everyday Things. Basic Books.
Rubin, J., & Chisnell, D. (2008). Handbook of Usability Testing. Wiley.
Additional sources on UX research methodologies and e-commerce usability.
Propose design solutions to address these barriers and painpoints.
Risk Criteria
1. Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
2. Frequency (# occurrence)
Onboarding Prototype
Post user interviews and usability testing, we had a good understanding of the problem statement and the solutions required for the same. So we started working on the prototype. The tool used for designing the prototype was Moqups.
Background
For a research project at Northeastern University, we focused on the critical role of accessibility and heuristic evaluation in driving the online dropoff % and retention %. We analyzed data available online, performed heuristic evaluation, and interviewed real customers.
We selected ZARA for this study because of its global presence and the notable lack of accessibility in its user experience.
The identified accessibility issues were addressed keeping usability and WCAG 2.1 compliance standards.
What is WCAG 2.1 Compliance standards?
WCAG 2.2, which was published in October 2023, includes 9 new success criteria building upon WCAG 2.1 and 2.0, focusing on improving accessibility for users with cognitive and learning disabilities, low vision, and those using mobile devices. These additions aim to make web content more inclusive and easier to use by addressing areas like focus visibility, input modalities, and time-based interactions.
The identified accessibility issues were addressed through a comprehensive redesign, leading to improved usability and full compliance with WCAG 2.1 standards.
Selected Brand: Zara
Zara’s e-commerce website was selected as the use case due to its global reach and the critical importance of accessibility in its user experience. The website was evaluated against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards, with a focus on the core principles of perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness. The objectives include:
Conduct a heuristic evaluation of Zara’s website to identify accessibility barriers
Connect with users and understand experience painpoints
Challenges
“In 2021, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern…”
When coronavirus affected the offline shopping experience worldwide, people couldn’t resist the urge to shop online, and that’s when the reality hit hard. With approximately 1200 offline outlets being shut down, Zara faced a 44% sales slump in their business, making it a major cause of concern.
Refer to the January 2023 web portal screenshots
Busy Images combined with low-contrast navigation patterns increase the exploration journey for first-time users. Especially when you want the customer to explore your product offerings, they shouldn’t be searching for certain areas — the search bar, navigation links, and categories.
Complex Navigation
The website’s layout can be unintuitive, making it difficult for users to find specific categories or products efficiently.
According to Sciencedirect.com, “…navigational links should be visible within 5 seconds…”
Over-Reliance on Images
Zara heavily emphasizes visual elements, sometimes at the expense of clear text descriptions, making it harder for users to scan and browse quickly.
Research
Research Hypothesis
Implementing usability and accessibility improvements based on WCAG 2.1 standards will result in higher user satisfaction and task completion rates for Zara’s e-commerce website.
Research Methods
(A) Heuristic Evaluation
Team
Karthik Sharma
Diksha Rawat
Shikha Singh
Harshveen Kalsi
Tasks
1. Browsing products by category.
2. Searching for a specific item.
3. Adding items to the cart.
4. Completing the checkout process.
The website was rigorously tested against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards, focusing on key principles of perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness.
(B) User Interviews
Objective
To understand user behaviors and pain points when using Zara’s website.
Participants
5 participants (2 female, 3 male) aged 22–25, representing Zara’s target demographic.
Sample Questions
How often do you order from ZARA?
Can you describe your experience with ordering?
Did you spend more time than expected ordering online?
Are there any significant roadblocks in your way?
What are your views on the mobile app?
Sample Tasks
Add a product from the “x” category to your cart and finalize the payment.
Navigate to the “y” part of the platform
Raise a platform concern
Can you browse the “z” category products
Ethical Considerations
Informed Consent
All participants provided informed consent before participating in interviews and surveys.Anonymity
Participant data was anonymized to protect privacy.Data Security: Survey and interview data were stored securely and used only for research purposes.
Sample Empathy Mapping
Here’s a sample empathy map that I created to capture what the user said, felt, did, and thought during the interviews. This map helped us pinpoint the sources of user frustration.
(C) Feedback Analysis
We dived deep into customer reviews to identify user emotion patterns towards the online presence to find that Zara had a 2.08 star rating from 1,132 reviews, indicating that most customers are generally dissatisfied with their online platform experience.
”…Zara ranked 43th among Best Global Brands in the year 2023. It was ranked 25th in 2018 and has kept dropping ever since…”
Code Inspection
On inspecting the web portal code to identify the design intricacies, we found that certain spacings, layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly,y the choice of background image used was interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Research Findings
The evaluation revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation and checkout processes.
Users struggled with ambiguous labels, inconsistent design, and a lack of feedback, leading to frustration and task abandonment.
These findings align with previous research on e-commerce usability, emphasizing the importance of clear navigation and error prevention., Layouts, typography sizes, and most importantly, the choice of background image used, were interfering with some industry standard accessibility guidelines.
Solution
Improved Navigation
Updated layout features ample white space and evenly distributed information essential for guiding users through their intended actions.
Onboarding starts with Information Clarity.
As part of our UX revamp, the website now features an improved onboarding process. After each development release, new features that benefit the user will be presented to returning customers through modals. We chose modals because they direct the user’s attention to key information, allowing them to focus on the content while keeping the background out of focus..
Feature Improvement: Sticky Pane for Major User Actions
To enhance usability and streamline the user experience, we propose the implementation of a sticky pane on the right side of the website. This pane will occupy 20% of the screen real estate and provide quick access to the most commonly performed tasks, ensuring that key functionalities are always within reach. The sticky pane will remain visible as users scroll, offering consistent and intuitive navigation.
Improved Accessibility
Key actions are always visible, reducing the cognitive load on users.
Enhanced Efficiency
Users can perform common tasks without navigating through multiple pages.
Consistent Navigation
The sticky pane ensures that essential functionalities are always accessible, regardless of where the user is on the website.
User-Centric Design
By prioritizing the most frequently used tasks, the design aligns with user needs and behaviors.
The same usability task results showed a user confidence boost of 60% on average.
We carried out moderated usability testing, focusing on task-based evaluation and comparison to the original version, to validate the prototype's usability and functionality.
Participants were tasked with comparing the navigation and overall layout of Zara's website to our prototype. Subsequently, they were assigned specific tasks, such as locating an item and placing an order, allowing us to assess the user experience comprehensively.
Learnings
Enhancing an interface doesn't always necessitate an extensive budget or a complete overhaul. Sometimes, minor adjustments can wield a substantial impact.
This paper served as a reminder that even prominent brands with successful products and services can undergo significant improvement without incurring exorbitant costs.
Conclusion
This study employed a mixed-methods approach to evaluate the usability of Zara’s website, combining heuristic evaluation, user interviews, and surveys. The findings revealed significant usability issues, particularly in navigation, checkout, and product discovery. By addressing these issues, Zara can enhance the user experience, increase customer satisfaction, and improve conversion rates. Future research could include usability testing with prototypes to validate the proposed recommendations.
References
Nielsen, J. (1994). Usability Engineering. Morgan Kaufmann.
Norman, D. A. (2013). The Design of Everyday Things. Basic Books.
Rubin, J., & Chisnell, D. (2008). Handbook of Usability Testing. Wiley.
Additional sources on UX research methodologies and e-commerce usability.
Propose design solutions to address these barriers and painpoints.
Risk Criteria
1. Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
2. Frequency (# occurrence)
Onboarding Prototype
Post user interviews and usability testing, we had a good understanding of the problem statement and the solutions required for the same. So we started working on the prototype. The tool used for designing the prototype was Moqups.